How to Record WebRTC in 3 Steps
WebRTC is an open-source project which makes it conceivable to add ongoing correspondence highlights to record WebRTC streams, for example, live video calls straightforwardly into the program applications and sites. Regularly utilized by various enterprises like banking and account, medical care, and schooling, it's a bunch of JavaScript APIs for recording WebRTC screen for a simple reconciliation without managing the intrinsic intricacies of requiring downloads or modules to utilize them. In any case, there are a couple of abilities that are not locally accessible in the WebRTC stack like account. To install the account work, the developers would normally utilize one of the accompanying techniques relying upon the innovation stack utilized for facilitating the WebRTC application and the ranges of abilities of the designers.
WebRTC Features
WebRTC is an overall standard created by the W3C consortium which chiefly centers around empowering Real-Time Communications over the web. Maybe, the best part about WebRTC is that it is free, open-source, and follows P2P usefulness. Every one of the continuous interchanges completed by WebRTC happens over Peer-to-Peer associations. Other than that, WebRTC utilizes HTML5 for setting up these associations.
- WebRTC looked significantly more encouraging from the current/future help point of view. With Firefox, Chrome, and Opera on work area previously having strong help, Microsoft declaring
- WebRTC 1.0 helps in Edge and Android's Chrome/Internet previously supporting it the pressing factor was on Apple and Safari to add support which they did as of late with Safari 11 presently in beta.
- WebRTC had another significant advantage: since it works by gushing there is no transfer time and there is no information misfortune in the event of program/crash and these advantages fixed the choice for us.
Server-side Recording of WebRTC
For the worker side chronicle, the media is steered utilizing a media worker rather than straightforwardly between the programs. For this situation, the WebRTC meeting is ended over the cuts off on the two closures with the media directed to the less than desirable end. The decoded media is then at the same time shipped off post-handling and recording. Specialist organizations with worker side account APIs permit the designers to do the accompanying:
Server-Side WebRTC Features
- Recording video/audio stream for each participant in the WebRTC session. These sessions could either be one-to-one or multi-party.
- Mixing and transcoding all participants’ streams into a single composite video file.
- Providing lay-outing API to manage the recording content layout.
- Additionally, there can be additional features such as integrating chat with recording, watermarking, etc. which are often required for recreating the session as it happened and for copyrighting
Steps to Record WebRTC
The processing involves the following steps:
Step 1. Multiplexing of information is finished. I.e., the media contributions from different clients are joined to frame a solitary media record which is then communicated over the worker to the end clients.
Step 2. Changes in design happen. I.e., in the wake of making the media record which is to be sent over to the worker, media changes should be possible to give an ideal arrangement to the media document.
Step 3. File compression happens. I.e., before transmission, the information can be compacted to lessen the record size. takes place.
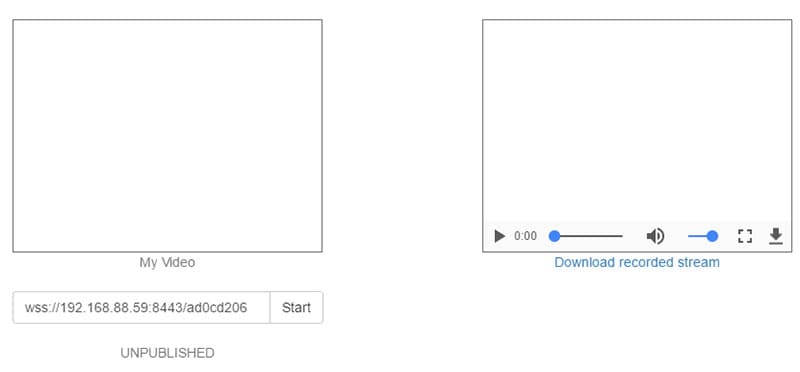
Client-side Recording of WebRTC
For customer side chronicle, recordings are recorded locally, and afterward handled before transferring to the workers. For this situation, an extra customer endpoint is expected to associate with the WebRTC meeting. This end-point is relied upon to introduce a product twofold containing the account programming picture. The product could either be offered as a docker picture or a straightforward ISO. One particular burden is that you can't handle the customer's endpoint and its presentation extraordinarily fluctuates as per the endpoint determinations. Enormous scope meetings require a top-of-the-line machine with a quick plate I/O access rate and a quick CPU.
Steps to Record WebRTC at Client Side:
The Client-side recording involves the following steps:
First of all, the videos are recorded and stored in local storage since WebRTC allows recording and storing video streams locally.
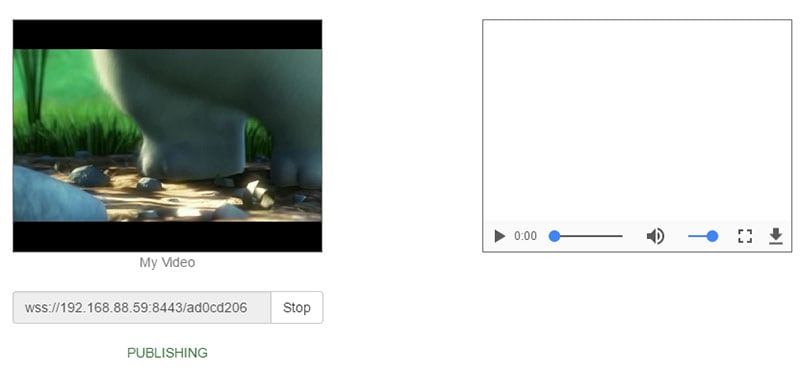
The recorded media is then uploaded to the servers.
Before uploading it to the server, the stored video file may be passed through the post-processing as done in the case of server-side videos.
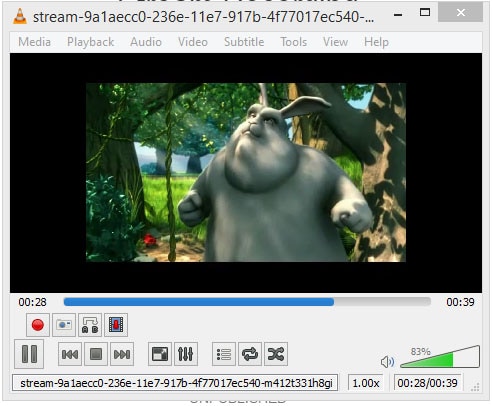
Media Forwarding and Remote Access
Video meetings are tied in with imparting. Meeting members do enthusiastically share what is caught by their webcam. With regards to security and classification, webcam accounts are an extraordinary matter. Far off Access is the point at which you distantly access another PC using WebRTC. You could have unlimited oversight of the far-off have, or possibly a solitary application. This is incredible for running computationally costly errands when the neighborhood equipment can't do it. Like running another computer game, or CAD programming. WebRTC being accessible in the program has been a colossal personal satisfaction improvement. You don't need to download an exclusive customer to begin the meeting. An ever-increasing number of customers are accompanying WebRTC packaged, shrewd TVs are getting full internet browsers now.
How is a WebRTC-based webcam recorder a protection issue, you may ponder? It is a result of the way that the cloud-based webcam recorder is worked by an outsider: the online webcam recording business. This outsider is a "man in the center" between your clients and your organization, who will approach all recordings that are being recorded, transcoded, and put away. Any approaching video goes through these client-side preparing steps. Just once done it tends to be sent to the site whose guests have presented the recordings.
Things to Remember When Recording WebRTC
Many think WebRTC is the only innovation for conferencing in the internet browser. It is far beyond that, however! WebRTC is utilized for a wide scope of utilization cases. New use cases appearing constantly. In this part we will show some normal ones and how WebRTC is upsetting them.
Multiparty Sessions
In a multiparty meeting, the likelihood of clients not having sufficient transfer speed to get the entirety of the members' video transfers, is high. In practical cases, a portion of the members' video quality will below. Thus, video recording quality, whenever done exclusively at the customer end will likewise have lower quality. For such cases, it is prescribed to go for a specialist organization offering worker side chronicle
Simultaneous Sessions
For various simultaneous meetings, load adjusting is required. In such cases, it is prescribed to go for a worker side chronicle to abstain from managing the intricacy of burden adjusting and recording the board in your application layer.
One-to-one Sessions
Since transfer speed may not be a test here, you can pick customer side or worker side account contingent upon whether you lean toward introducing a chronicle worker at your end and manage all chronicle the executives’ issues.
Distributed Peer-to-Peer Session
WebRTC is a decentralized media convention that permits media and information to be traded straightforwardly between peers. In a standard distributed (P2P) association model, all members interface with one another in what's known as a cross-section design. The entirety of the preparation of the media happens on the equipment at one or the flip side of the association.
This solitary works to a certain degree, when the processor begins to run out of ability to deal with the entirety of the streams that are being sent and gotten from the entirety of different companions. When you have such a large number of endpoints associated with one another in this style things begin to separate.